In this article, we will explore the various factors that can impact your credit score and discuss ways to address them. Understanding these factors will help you take control of your credit and improve your financial health. We will discuss the importance of timely payments, credit utilization, length of credit history, and the impact of credit inquiries. By the end of this article, you will have a clear understanding of how these factors affect your credit score and the steps you can take to maintain or improve it.
This image is property of www.investopedia.com.
Understanding Credit Scores
What is a credit score?
Your credit score is a three-digit number that represents your creditworthiness and financial health. It is a numerical evaluation of your credit history and serves as a tool for lenders to assess the risk of lending money to you.
Why is it important?
Having a good credit score is essential for various financial activities, such as getting a loan, renting an apartment, or even applying for a credit card. Lenders use your credit score to determine the interest rates they will offer you, and a higher credit score can result in better terms and conditions for loans and other financial products.
How is it calculated?
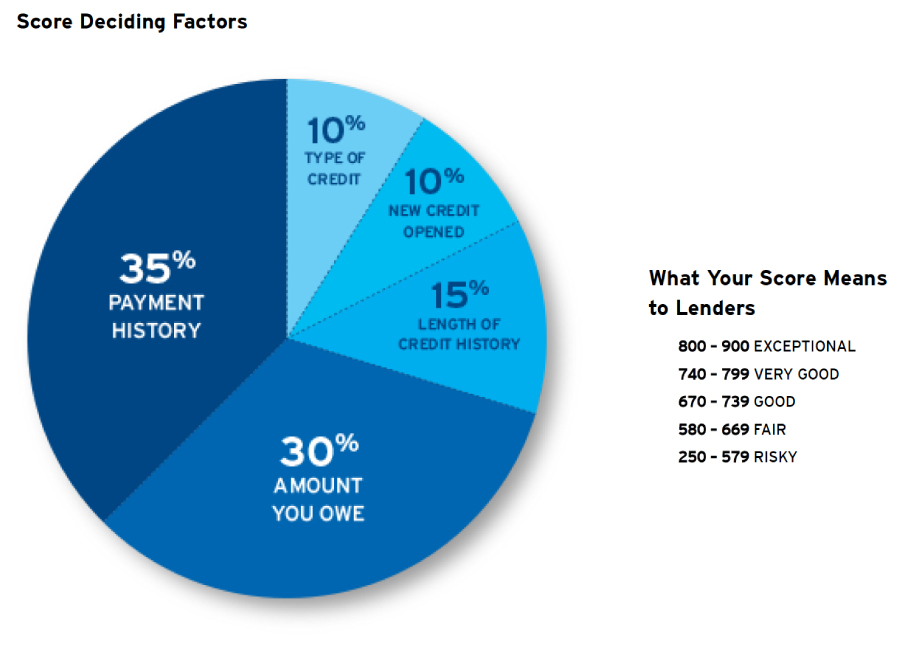
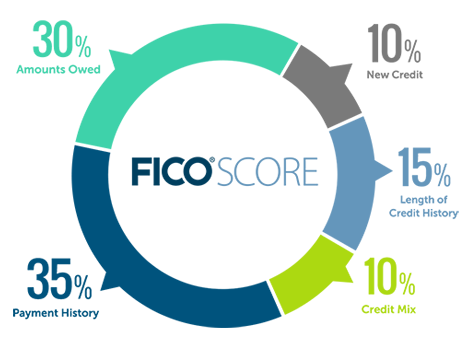
Credit scores are calculated using complex algorithms that take into account several factors from your credit history. While the exact formula varies between credit bureaus, the most widely used credit scoring model is the FICO score. Here are some key factors that influence your credit score.
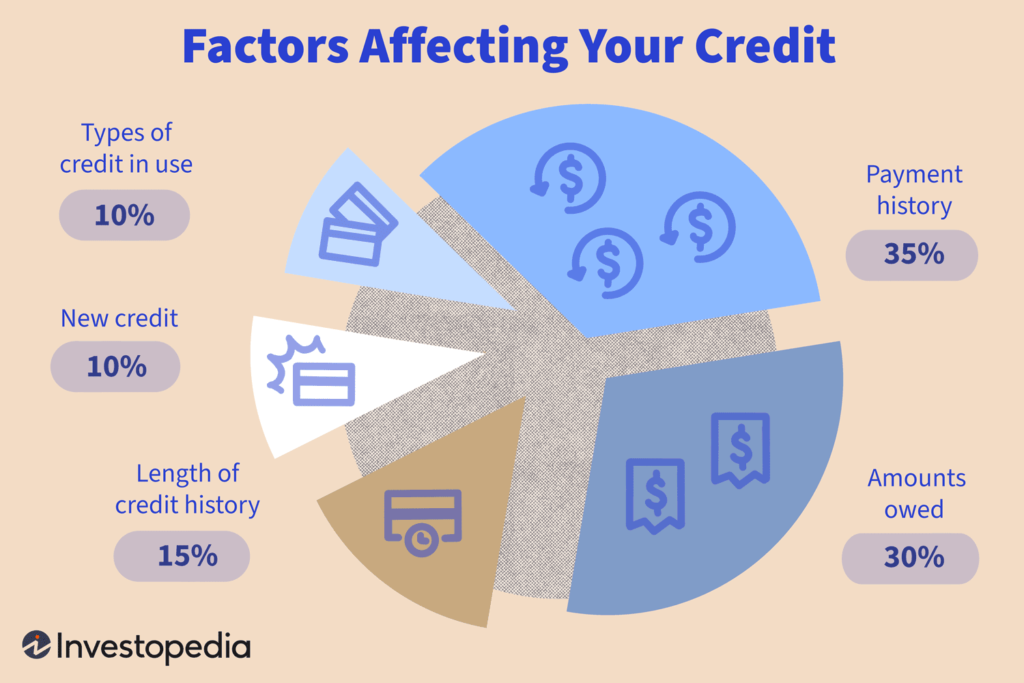
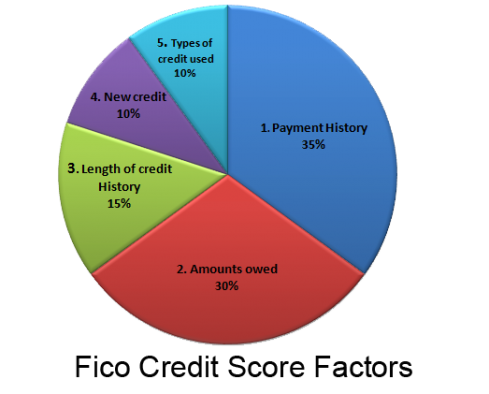
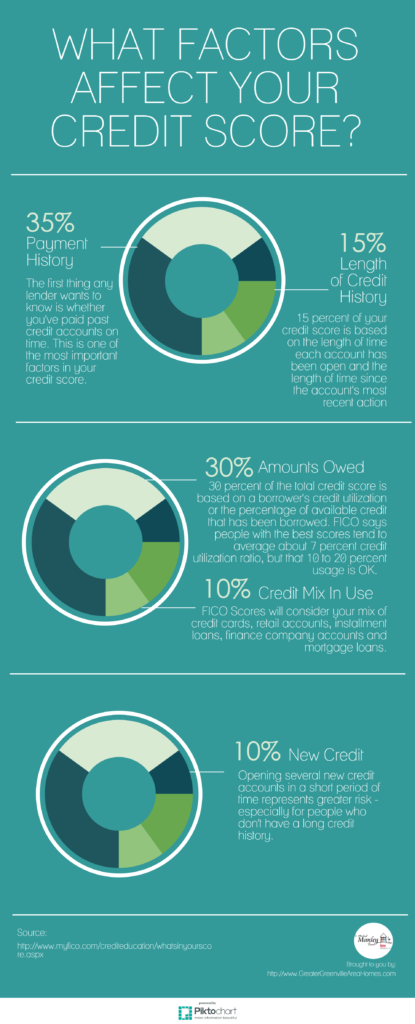
Factors that Affect Credit Scores
Payment history
Your payment history is the most significant factor that affects your credit score. It reflects whether you make your payments on time, including credit card bills, loan installments, and other debts. Late payments or defaults can have a significant negative impact on your credit score.
Credit utilization
Credit utilization refers to the percentage of your available credit that you are currently using. High credit utilization suggests that you are relying heavily on credit and may be a potential risk to lenders. It is generally advisable to keep your credit utilization below 30% to maintain a good credit score.
Length of credit history
The length of your credit history also plays a crucial role in determining your credit score. Lenders typically prefer borrowers with a longer credit history, as it gives them a more accurate picture of your financial habits and behavior over time.
Credit mix
Having a diverse credit mix can positively impact your credit score. It shows lenders that you can handle different types of credit responsibly. This mix can include credit cards, loans, mortgages, and other forms of credit.
New credit inquiries
Every time you apply for new credit, such as a loan or credit card, the lender may perform a hard inquiry on your credit report. Too many inquiries within a short period can have a negative impact on your credit score, as it suggests that you may be seeking credit in desperation.
Addressing Payment History Issues
Making timely payments
To improve your credit score, it is crucial to make all of your payments on time. Late payments can be detrimental to your credit history and may stay on your credit report for up to seven years. Set up reminders or automatic payments to ensure you never miss a due date.
Negotiating payment plans
If you are struggling to make your payments, it is advisable to contact your creditors and discuss possible payment arrangements. They may be open to negotiating lower payments or extended repayment terms to help you manage your debts.
Utilizing automatic payments
Setting up automatic payments for your bills can be a convenient way to ensure that your payments are made on time. This method eliminates the chances of forgetfulness or oversight, giving you peace of mind that your credit responsibilities are being met.
Managing Credit Utilization
Paying off balances regularly
To maintain a healthy credit score, it is recommended to pay off your credit card balances in full each month. This not only helps you avoid unnecessary interest charges but also keeps your credit utilization low.
Increasing credit limit
Another way to manage credit utilization is by requesting a credit limit increase on your credit cards. As long as you don’t increase your spending, a higher credit limit will automatically lower your credit utilization ratio.
Avoiding unnecessary credit applications
Each time you apply for new credit, it results in a hard inquiry on your credit report. To minimize the impact on your credit score, be selective with credit applications and only apply for credit when necessary.
This image is property of beehive.org.
Building a Positive Credit History
Keeping accounts open
Keeping your credit accounts open, even if you no longer use them, can positively impact your credit score. Closing old accounts can reduce the average age of your credit history and potentially lower your score.
Avoiding closing old accounts
As mentioned earlier, closing old accounts can have a negative impact on your credit score. If you have old credit cards with no outstanding balances, it is generally advisable to keep them open to maintain a longer credit history.
Being cautious with new credit
While building credit is crucial, it is important to be cautious when taking on new credit. Only take on credit that you can manage responsibly, and avoid opening multiple new accounts within a short period.
Establishing diverse credit mix
To further strengthen your credit score, consider establishing a diverse credit mix. Having different types of credit, such as credit cards, loans, and mortgages, displays your ability to handle various financial obligations responsibly.
Dealing with Credit Mix Challenges
Adding different types of credit
If your credit mix is limited, you can improve it by adding different types of credit. For example, if you only have credit cards, consider applying for a small personal loan or a mortgage to diversify your credit portfolio.
Seeking professional advice
If you face challenges in managing your credit mix or have concerns about your overall credit score, it can be beneficial to seek professional advice. Credit counselors can help you develop a personalized plan to address your specific credit-related issues.
This image is property of bt-wpstatic.freetls.fastly.net.
Minimizing the Impact of New Credit Inquiries
Being selective with credit applications
To minimize the negative impact of new credit inquiries, only apply for credit when necessary. Before applying, research the requirements and qualifications to ensure that you meet the lender’s criteria and have a good chance of approval.
Monitoring credit reports for accuracy
Regularly monitoring your credit reports allows you to identify any inaccuracies or unauthorized inquiries promptly. If you notice any discrepancies, you can dispute them with the credit bureaus to have them corrected.
Additional Steps for Credit Improvement
Checking credit reports regularly
Checking your credit reports regularly is crucial for understanding your financial standing. By reviewing them, you can identify any potential issues, errors, or signs of fraud that may be negatively impacting your credit score.
Disputing inaccuracies
If you find any inaccuracies or errors on your credit reports, contact the credit bureaus to dispute them. Providing documentation and explaining the discrepancy can help correct any incorrect information and improve your credit score.
Reducing debt
Reducing your debt is an effective way to improve your credit score. Develop a debt repayment plan and prioritize paying off high-interest debts first, such as credit card balances.
Seeking credit counseling
If you find it challenging to manage your debts or improve your credit score on your own, consider seeking credit counseling. A credit counselor can provide guidance on budgeting, debt management, and credit improvement strategies tailored to your specific situation.
This image is property of prosperopedia.com.
Understanding the Influence of Public Records
Bankruptcies
Bankruptcies have a significant negative impact on your credit score and can stay on your credit report for up to ten years. It is essential to avoid bankruptcy if possible, as it can severely limit your financial options.
Foreclosures
Foreclosures, which occur when a lender repossesses a property due to non-payment, also have a detrimental effect on your credit score. They can stay on your credit report for up to seven years and make it difficult to qualify for future loans or mortgages.
Tax liens
Unpaid tax liens can be reported on your credit report and negatively affect your credit score. They can stay on your credit report for up to seven years. It is essential to resolve any tax liens promptly to minimize their impact on your credit score.
Civil judgments
Civil judgments, typically involving unpaid debts resulting in legal action, can also impact your credit score. They can stay on your credit report for up to seven years. It is crucial to address and resolve civil judgments to improve your creditworthiness.
Conclusion
Taking control of your credit score is essential for your financial well-being. By understanding the factors that influence your credit score, such as payment history, credit utilization, length of credit history, credit mix, and new credit inquiries, you can address any issues and improve your creditworthiness. By making timely payments, managing your credit utilization, and maintaining a positive credit history, you can strengthen your credit score and open up opportunities for better financial products and terms. Remember to regularly monitor your credit reports, dispute inaccuracies, and seek professional guidance if needed. By addressing and improving these credit factors, you can take charge of your credit score and secure a brighter financial future.
This image is property of www.myfico.com.