So you’ve heard of MVP funding, but you’re not quite sure if it’s the right option for you. Well, look no further! In this article, we’ll be exploring the pros and cons of MVP funding, also known as bad credit loans. Whether you’re in need of some quick cash or trying to rebuild your credit, understanding the advantages and disadvantages of this type of funding can help you make an informed decision. So grab a cup of coffee, sit back, and let’s dive into the world of MVP funding.
This image is property of keyua.org.
What is MVP Funding?
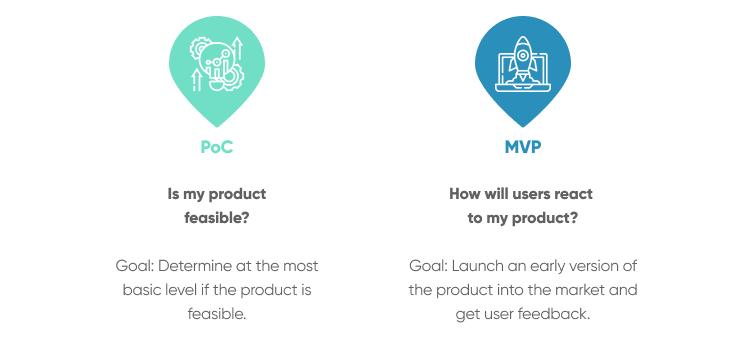
MVP, or Minimum Viable Product, funding refers to the financing obtained by startups or entrepreneurs to develop and launch their initial product or service. It is a concept popularized by the Lean Startup methodology, which emphasizes the importance of validating a product’s market viability and addressing customer needs before committing extensive resources.
Definition of MVP Funding
MVP Funding is the financial support provided to entrepreneurs to develop a minimum viable product, which is the most basic version of their product or service that can still provide value to customers. This initial version focuses on delivering core features and functionality rather than aiming for a fully polished product.
Importance of MVP Funding
MVP funding plays a crucial role in the early stages of a startup by providing the necessary resources to develop and test a minimum viable product. It enables entrepreneurs to gather initial market feedback, validate their product’s viability, and make informed decisions about further development and investment.
By securing MVP funding, startups can reduce financial risk and attract potential investors who are more interested in supporting ventures with a proven market demand. It allows entrepreneurs to focus on building a solid foundation for their business, increasing the likelihood of success in the long run.
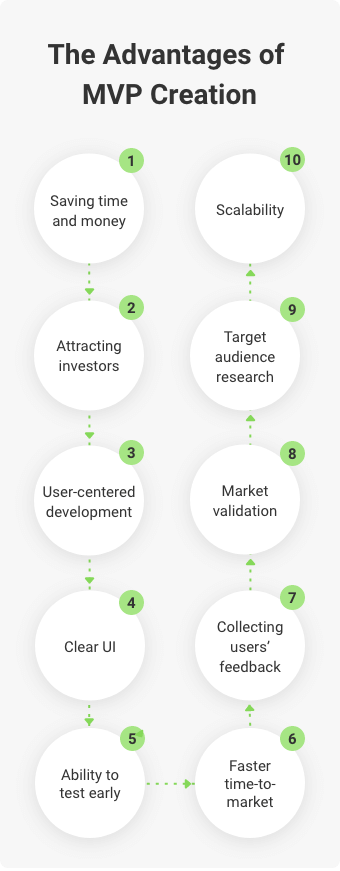
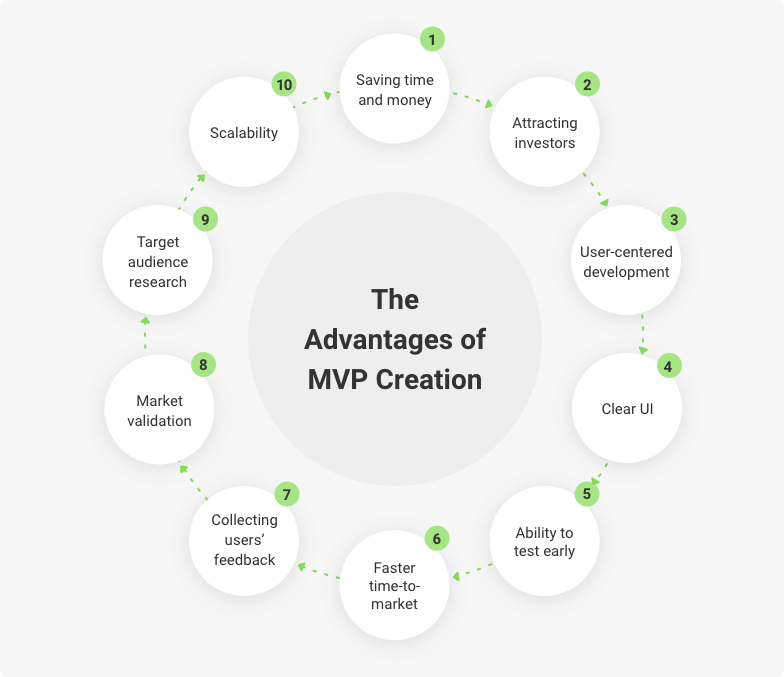
Pros of MVP Funding
1. Quick Access to Funds
MVP funding offers startups quick access to financial resources, allowing them to commence product development without significant delays. This funding may come from various sources, such as angel investors, crowdfunding campaigns, or venture capital firms, enabling entrepreneurs to kickstart their projects and avoid lengthy fundraising processes.
2. Opportunity for Early Market Validation
Developing a minimum viable product provides an opportunity to validate the market demand for a product or service. By launching a simplified version of their offering, startups can gather valuable feedback from early adopters and make necessary adjustments before investing further in product development. This early validation helps minimize the risk of building a product that does not resonate with the target audience.
3. Ability to Iterate and Improve
MVP funding enables startups to adopt an iterative development approach. By releasing an initial version of their product or service, entrepreneurs can gather user feedback, identify areas for improvement, and make iterative changes based on real-world usage. This agile methodology allows for continuous improvement while maximizing resource efficiency.
4. Lower Financial Risk
Securing MVP funding mitigates the financial risk associated with building a full-scale product without any market validation. By launching a minimum viable product, entrepreneurs can assess market demand and the potential return on investment before committing substantial resources to further development. This approach minimizes the risk of financial failure and wasted resources.
5. Increased Investor Interest
With a validated minimum viable product, startups gain credibility and become more attractive to potential investors. By demonstrating product-market fit and proving there is demand, startups are more likely to secure additional funding to scale their operations. MVP funding acts as a stepping stone, increasing investor interest and facilitating future fundraising efforts.
Cons of MVP Funding
1. Limited Scope and Functionality
Developing a minimum viable product often requires streamlining and simplifying the features and functionality compared to the final vision of the product. This can result in a limited scope and a less comprehensive user experience. While this minimalistic approach serves the purpose of validating market demand, it may not fully represent the long-term potential of the product.
2. Potential for Negative User Experience
Due to its simplified nature, a minimum viable product may lack the polish and refinement expected by users. This can result in a subpar user experience, potentially leading to negative feedback, lower adoption rates, and customer churn. It’s essential for entrepreneurs to manage user expectations and communicate the developmental nature of MVPs to mitigate potential negative impacts.
3. Resources and Time Constraints
Developing and launching a minimum viable product with limited funding often means working with restricted resources and tight timelines. Startups may face challenges in hiring talent, acquiring necessary tools and technologies, and meeting aggressive deadlines. Efficient resource allocation and effective project management become crucial to successfully navigate these constraints.
4. Pressure to Deliver Results
With MVP funding, startups face the pressure to deliver tangible results and demonstrate progress within a limited timeframe. Meeting expectations and achieving key milestones can be demanding, requiring a high level of focus and commitment from the entrepreneurial team. This pressure can lead to stress and burnout if not managed effectively.
5. Increased Competition
The accessibility of MVP funding has led to a surge in startups and entrepreneurs vying for limited investment opportunities. This increased competition poses challenges for securing funding, as investors have a wide range of options to choose from. Startups need to differentiate themselves and demonstrate a unique value proposition to stand out in the crowded startup landscape.
Factors to Consider Before Seeking MVP Funding
1. Market Research and Validation
Before seeking MVP funding, startups must thoroughly research their target market and validate their product’s potential market fit. Understanding the needs, preferences, and pain points of customers is essential to ensure the viability and demand for the intended product or service.
2. Cost Analysis
Conducting a comprehensive cost analysis is crucial to determine the funding requirements for developing and launching a minimum viable product. Startups must consider expenses related to development, marketing, operations, and any unforeseen contingencies to estimate the funding needed accurately.
3. Clear Product Vision
Having a clear product vision ensures that all stakeholders understand the goals and objectives of the minimum viable product. Entrepreneurs must articulate their vision and define the core features and functionality that will be delivered in the initial version. This clarity guides the development process and facilitates effective communication with investors and team members.
4. Competitor Analysis
Analyzing the competitive landscape helps identify potential gaps and opportunities for differentiation. Startups need to identify their competitors, understand their strengths and weaknesses, and determine how they can position their minimum viable product to stand out in the market.
5. Team and Skills Assessment
Evaluating and assessing the capabilities and expertise of the entrepreneurial team is crucial before seeking MVP funding. Startups need to ensure they have the right skills and resources to develop and launch the product successfully. Identifying any skill gaps and determining how to address them is essential for the efficient execution of the project.
This image is property of www.softkraft.co.
Alternatives to MVP Funding
1. Bootstrapping
Bootstrapping involves self-funding the development and launch of a startup without relying on external investors or funding sources. This approach allows entrepreneurs to retain full control over their business but may limit the speed and scale of growth due to resource constraints.
2. Crowdfunding
Crowdfunding platforms enable startups to raise funds from a large number of individuals who believe in their product or vision. This approach allows for early validation and access to a potentially large pool of supporters. However, it requires effective marketing and storytelling to attract backers and successfully reach funding goals.
3. Angel Investors
Angel investors are individuals who provide early-stage funding to startups in exchange for equity or debt. These investors often bring valuable expertise and industry connections, in addition to financial support. Partnering with angel investors can provide startups with not only capital but also guidance and mentorship.
4. Venture Capital
Venture capital firms invest in startups with high growth potential in exchange for equity. They typically provide larger funding amounts compared to angel investors, making them suitable for startups aiming to scale rapidly. However, venture capital investment often comes with high expectations and increased pressure for growth and profitability.
5. Grants and Government Funding
Startups can explore grants and government funding programs that support innovation and entrepreneurial ventures. These programs provide non-dilutive funding, meaning entrepreneurs do not have to give up equity. However, securing grants can be highly competitive and requires meeting specific eligibility criteria and compliance requirements.
Successful Examples of MVP-funded Startups
1. Airbnb
Airbnb, a global online marketplace for accommodations, initially started as a minimum viable product. The founders rented out air mattresses in their apartment to test the concept and gather feedback. This approach allowed them to validate the demand and refine their business model before securing significant funding.
2. Dropbox
Dropbox, a cloud storage and file-sharing service, also began as an MVP. Initially, the founders created a simple video demonstration showcasing the product’s potential, allowing them to gauge user interest and secure early adopters. This early validation was crucial in attracting investors and scaling the business.
3. Twitter
Twitter, the popular social media platform, started as a side project within a podcasting company. The founders launched a minimum viable product as a simple SMS-based messaging service, which gained traction and validated the demand for real-time microblogging. This MVP approach laid the foundation for Twitter’s subsequent growth and success.
4. Uber
Uber, the ride-hailing service, is another prime example of leveraging MVP funding. The initial version of the app focused on connecting users with professional drivers. By launching in a limited location and refining their model based on user feedback, they were able to prove the business concept and attract substantial funding.
5. Spotify
Spotify, the popular music streaming service, originally launched as an MVP to offer a legal alternative to illegal music downloading. The founders secured licensing agreements with record labels for a limited catalog of music, allowing them to validate the market demand and refine their product before expanding their music library.

This image is property of keenethics.com.
Case Studies: MVP Funding in Action
1. Case Study 1: Company X
Company X, a technology startup, utilized MVP funding to develop a mobile app for remote work collaboration. By launching an initial version with core features like document sharing and real-time communication, the startup gathered user feedback and iteratively improved the app. This agile approach enabled Company X to secure additional funding and eventually expand to a fully-featured collaboration platform.
2. Case Study 2: Company Y
Company Y, an e-commerce startup, secured MVP funding to build an online marketplace connecting local artisans with customers. By initially focusing on a specific geographic area and a limited product range, Company Y validated the market demand and refined their platform’s user experience. This MVP approach attracted early adopters and investor interest, leading to further funding rounds for expansion.
3. Case Study 3: Company Z
Company Z, a healthcare technology startup, leveraged MVP funding to develop a telemedicine platform. By launching a basic version with video consultation functionality, Company Z was able to assess user feedback, refine their service, and expand to additional features like appointment scheduling and online prescriptions. This iterative approach allowed the startup to demonstrate market demand and secure partnerships with healthcare providers.
Tips for Making the Most of MVP Funding
1. Set Clear Goals and Milestones
Define clear goals and milestones for your minimum viable product. Establishing measurable objectives helps track progress and evaluate the success of your MVP. Clearly define what you aim to achieve with your initial product iteration, whether it be user acquisition, revenue validation, or market share growth.
2. Prioritize Features and Functionality
Focus on building and launching core features that address the most critical customer needs. Prioritizing functionality helps streamline development efforts and ensures you deliver the most valuable aspects of your product or service to the market. Avoid feature creep and stay focused on the core value proposition of your minimum viable product.
3. Gather User Feedback and Iterate
Actively seek user feedback and iterate based on the insights gathered. Encourage early adopters to provide feedback, conduct user testing sessions, and leverage analytics to gather quantitative data. This feedback loop helps uncover user pain points, refine the user experience, and align your product roadmap with customer needs.
4. Build a Strong Support Network
Develop a network of mentors, advisors, and industry experts who can provide guidance and support throughout your MVP journey. Surrounding yourself with knowledgeable individuals who have experience in your industry can provide valuable insights and help navigate the challenges of product development and fundraising.
5. Plan for Future Growth
While focusing on the minimum viable product, do not lose sight of the long-term vision for your startup. Develop a roadmap for future growth, refining your product based on user feedback and market trends. Consider scalability, potential partnerships, and expansion possibilities to ensure your MVP sets you on a path for success beyond the initial launch.
This image is property of keyua.org.
Conclusion
MVP funding offers startups a valuable opportunity to develop and launch their initial products or services, providing quick access to funds and enabling early market validation. By considering the pros and cons of MVP funding and conducting thorough market research, startups can make informed decisions about seeking funding and develop successful minimum viable products. With careful planning, efficient resource allocation, and a focus on iterative improvement, startups can maximize the potential of MVP funding to accelerate their growth and secure future investment.