“Swipe Right on Credit: Millennial Mindsets in the Financial Landscape” explores the unique financial behaviors and outlooks of the millennial generation. Born between 1981 and 1996, millennials have experienced significant historical and cultural events that have shaped their attitudes towards money, from the Great Recession to the rise of the internet. This generation is characterized by their tech-savviness, focus on experiences, and desire for work-life balance. Despite facing challenges such as student debt and struggles with savings, millennials are determined to prioritize financial stability and make informed decisions. The article also compares millennials to the up-and-coming Generation Z and highlights the importance for financial institutions to recognize these generational differences in order to effectively serve their customers.
Understanding Millennials: Who Are They?
Millennials, born between 1981 and 1996, are a generation situated between Baby Boomers and Generation Z. What defines Millennials is not just their birth years, but also the historical and cultural events that have shaped their experiences. These events, such as the Great Recession, the rise of the internet, and the aftermath of 9/11, have influenced Millennials’ attitudes towards money and financial institutions. As a result, Millennials exhibit distinct characteristics and behaviors when it comes to finances.
Historical and Cultural Events Shaping Millennials
The historical events that Millennials have lived through have had a profound impact on their financial outlook. The Great Recession, for example, has made Millennials more cautious about their finances, leading them to prioritize saving and investing. Additionally, growing up in the age of technology has made Millennials digital natives. They prioritize convenience, efficiency, and the rapid adoption of digital financial tools. This has resulted in less brand loyalty to traditional financial institutions and a preference for tailored products and services.

This image is property of ml2fceqxldkb.i.optimole.com.
Distinct Characteristics of Millennials
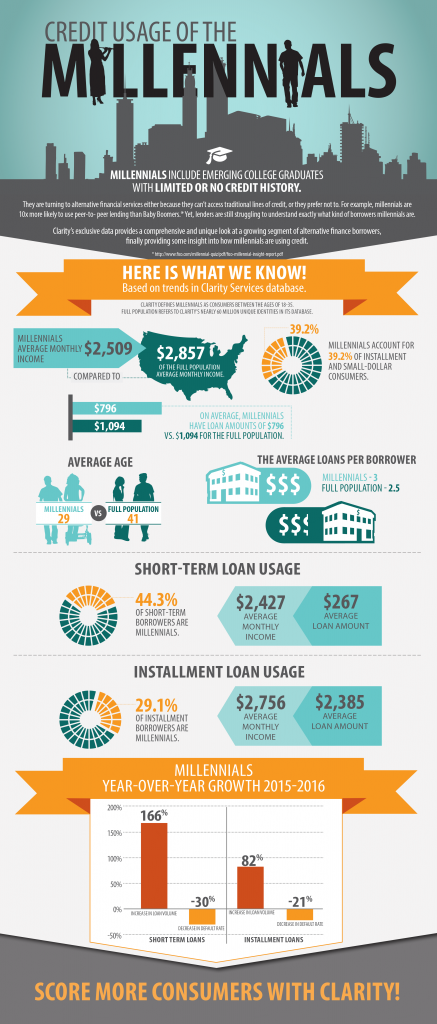
Millennials are known for their tech-savviness, focus on experiences, and emphasis on work-life balance. They are quick to adopt digital financial tools and services, such as mobile banking and online investing platforms. However, Millennials also face unique financial challenges, such as student debt and struggles with long-term savings. Despite these challenges, Millennials prioritize financial stability and strive to make informed financial decisions to achieve their goals.
Millennials and the Digital Revolution in Finance
Millennials have played a crucial role in the digital revolution in finance. Their affinity for technology has led to the widespread adoption of digital financial tools, such as mobile banking and digital payments. This, in turn, has prompted financial institutions to develop more advanced products and services to cater to Millennials’ digital preferences. The digital revolution has also opened doors for new financial products and services tailored to Millennials’ needs, such as credit-building tools that take alternative credit report data into account.
This image is property of www.zootsolutions.eu.
Millennials’ Adoption of Digital Financial Tools
Millennials’ tech literacy and preference for convenience have driven their rapid adoption of digital financial tools. They embrace mobile banking, digital payments, and online investing platforms at a faster pace than older generations. This has created a need for financial institutions to develop more advanced products and services to cater to Millennials’ digital preferences. Institutions that successfully adapt to these preferences can attract and retain Millennials as customers.
Millennials, Credit, and Financial Priorities
While Millennials prioritize financial stability, they face challenges in areas like credit and long-term savings. Factors such as student loan debt and credit card balances can impact their credit reports and impede their ability to make major purchases or qualify for loans with favorable terms. Managing credit responsibly and regularly reviewing credit reports are important steps for Millennials to improve their financial standing. Staying informed about their credit scores and taking proactive steps to achieve their financial goals can lead to a brighter financial future.
This image is property of evokad.com.
Comparing Millennials and Gen Z: Financial Outlooks
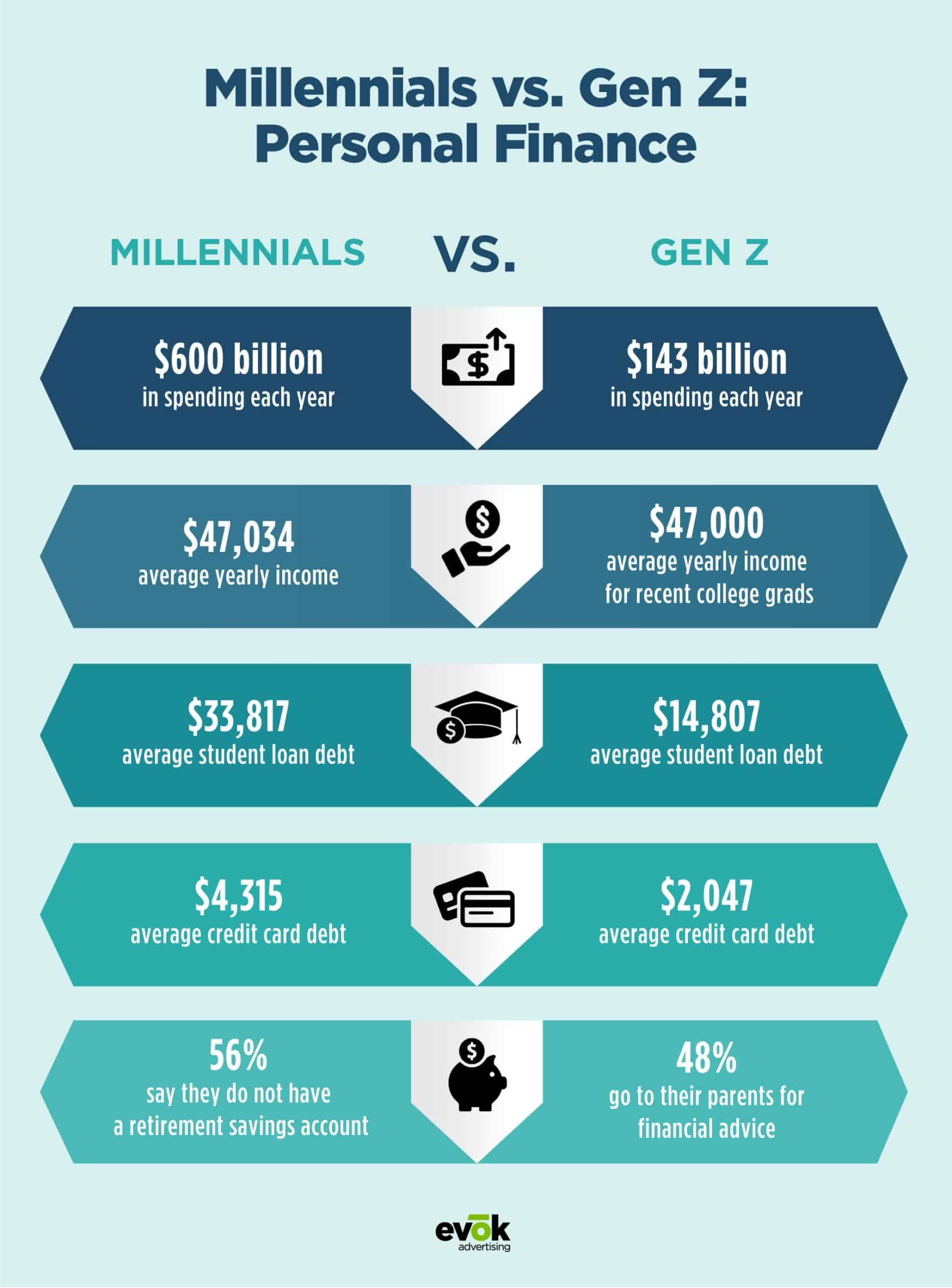
Compared to Millennials, Generation Z, born between 1997 and 2012, exhibits different financial outlooks. Growing up in a world of rapid technological advancements and economic recovery, Gen Z approaches finances with a more cautious mindset. They prioritize avoiding debt and saving for the future, likely influenced by witnessing the financial struggles faced by Millennials. Financial institutions must understand Gen Z’s distinct needs and priorities to better serve this emerging demographic.
Defining Gen Z’s Financial Behavior
Gen Z’s financial behavior is characterized by a pragmatic approach to money management. They prioritize saving and avoiding debt, reflecting the lessons learned from the financial struggles of previous generations. As Gen Z begins to establish their financial footprint, it is crucial for financial institutions to recognize and adapt to their unique needs and preferences. By offering tailored products and services, institutions can foster long-term relationships with this emerging generation.
This image is property of cdn.newsday.com.
Implications of Generational Differences in Finance
Understanding generational differences in finance is essential for financial institutions seeking to serve a diverse customer base. By recognizing the distinct needs and preferences of each generation, institutions can tailor their offerings and marketing strategies. However, it is important to acknowledge that generational categories are not the sole determinant of an individual’s financial behavior. Life stage, personal goals, and financial circumstances also play significant roles and should be considered when developing strategies to serve customers effectively.
Why Generational Cohort Names Matter in Financial Services
Generational cohort names, such as Millennials and Gen Z, provide a convenient way for financial service providers to understand the attitudes, motivations, and behaviors of specific age groups. By recognizing the unique financial outlooks and preferences of each generation, institutions can tailor their offerings and marketing strategies accordingly. This understanding can help build stronger relationships with customers and drive business growth. However, it is crucial to consider additional factors beyond generational categories to fully understand individuals’ financial behavior.
This image is property of qph.cf2.quoracdn.net.
Tech Adaptation in Finance Across Generations
Technology adoption varies across generations, with younger cohorts like Millennials and Gen Z embracing digital financial tools more quickly than older ones. Financial institutions must adapt and innovate to meet the evolving needs of their customers. By offering cutting-edge digital solutions and a seamless user experience, institutions can attract and retain customers across generations. Staying ahead of the competition requires continuously adapting to advancements in technology and meeting customers’ ever-changing expectations.
Challenging the Generational Paradigm in Financial Decisions
While generational differences provide valuable insights, it is important to recognize that age-based categories alone may not fully capture an individual’s financial behavior and needs. Factors such as life stage, personal goals, and financial circumstances play significant roles in shaping financial decisions. Financial institutions should take a personalized approach, considering these additional factors to better serve customers and help them achieve their financial objectives. By doing so, institutions can foster stronger relationships and provide more effective support.
Validity of Age-Based Financial Strategies
Age-based financial strategies can provide guidance for financial decision-making, but they may overlook the diverse experiences and priorities within a generation. To ensure the effectiveness of financial strategies, it is crucial to consider the unique financial goals, needs, and circumstances of individuals. A personalized approach that takes into account the individual’s situation will result in better solutions and support to help them achieve their financial objectives.
Interplay Between Age, Life Stage, and Financial Decisions
The interplay between age, life stage, and financial decisions is complex. Factors such as cognitive abilities, experience, and individual circumstances all play a role. As individuals progress through different life stages, their financial goals and needs evolve. Financial institutions must recognize and understand this interplay when designing products and services. By doing so, they can provide more effective support and guidance at every stage of their customers’ lives.
Summary
Millennials have shaped the financial landscape through their adoption of digital financial tools and their unique financial outlooks. Comparing Millennials to Generation Z reveals distinct differences in financial behavior and priorities. Financial institutions must recognize and adapt to these generational differences while also considering factors beyond age, such as life stage and personal goals. By serving their diverse customer base effectively, institutions can foster stronger relationships and help individuals achieve their financial goals.