In 2023, the average credit score in the US is 714, according to Experian data from Q3 2022. This marks a gradual increase in average credit scores since the 2008 recession. However, it’s important to note that credit scores fluctuate monthly, and individual lenders have their own range of credit scores they consider to be good. Currently, 67 percent of Americans have credit scores between 670 and 850, which are considered good to excellent. Those with scores under 670 may face difficulties being approved for loans and could be subject to higher interest rates. Overall, understanding the average credit score can provide valuable insights into the lending landscape.
This image is property of www.lexingtonlaw.com.
The Meaning and Significance of Credit Score
Understanding credit score
When it comes to your financial health, your credit score plays a significant role. But what exactly is a credit score? In simple terms, it is a three-digit number that represents your creditworthiness. It reflects how likely you are to repay your debts based on your past borrowing behavior. Lenders, such as banks and credit card companies, use this score to assess the risk of lending you money.
Relevance of credit score in financial transactions
From applying for a mortgage or car loan to getting approved for a credit card or even renting an apartment, your credit score can have a profound impact on your financial transactions. A good credit score can open doors to better interest rates, higher credit limits, and more favorable loan terms. On the other hand, a poor credit score can lead to higher interest rates, limited borrowing options, and even denials.
The range of credit scores and their implications
Credit scores typically range from 300 to 850, with higher scores indicating lower credit risk. Here’s a breakdown of the credit score ranges and their implications:
-
Excellent (800-850): Individuals with excellent credit scores are likely to qualify for the best interest rates and terms. They have a strong history of on-time payments and responsible credit management.
-
Very Good (740-799): This range is considered very good, and individuals falling within it are also likely to receive favorable interest rates and terms.
-
Good (670-739): A credit score in this range is considered good and generally means that individuals have a solid credit history.
-
Fair (580-669): Scores in this range may indicate some credit issues or a limited credit history. Interest rates and terms may not be as favorable.
-
Poor (300-579): Individuals with scores in this range may face significant difficulties in obtaining credit or may be required to pay high interest rates and fees.
Understanding your credit score range can help you determine how lenders might perceive your creditworthiness and what steps you might need to take to improve your score if necessary.
FICO and VantageScore: The Two Predominant Scoring Models
Overview of FICO scoring model
FICO, short for Fair Isaac Corporation, is one of the most widely used credit scoring models in the United States. It was introduced in the 1950s and has become the industry standard for assessing credit risk. FICO scores range from 300 to 850 and are based on various factors such as payment history, credit utilization, length of credit history, types of credit used, and new credit accounts.
Overview of VantageScore scoring model
VantageScore is another commonly used credit scoring model. It was developed by the three major credit bureaus (Experian, Equifax, and TransUnion) as a competitor to FICO. VantageScores also range from 300 to 850 and consider similar factors as FICO, but with slight differences in their scoring algorithms. One notable feature is that VantageScore takes into account a shorter credit history, which can benefit individuals with limited credit histories.
Comparing FICO and VantageScore
While FICO and VantageScore use different algorithms to calculate credit scores, they both aim to assess credit risk. Ultimately, the differences between the two models may result in slightly different credit scores for individuals. However, most lenders consider both scores when evaluating creditworthiness. It’s important to note that not all lenders use the same scoring models, so it’s possible that your FICO score and VantageScore may differ slightly depending on the lender and the credit bureau’s data they use.
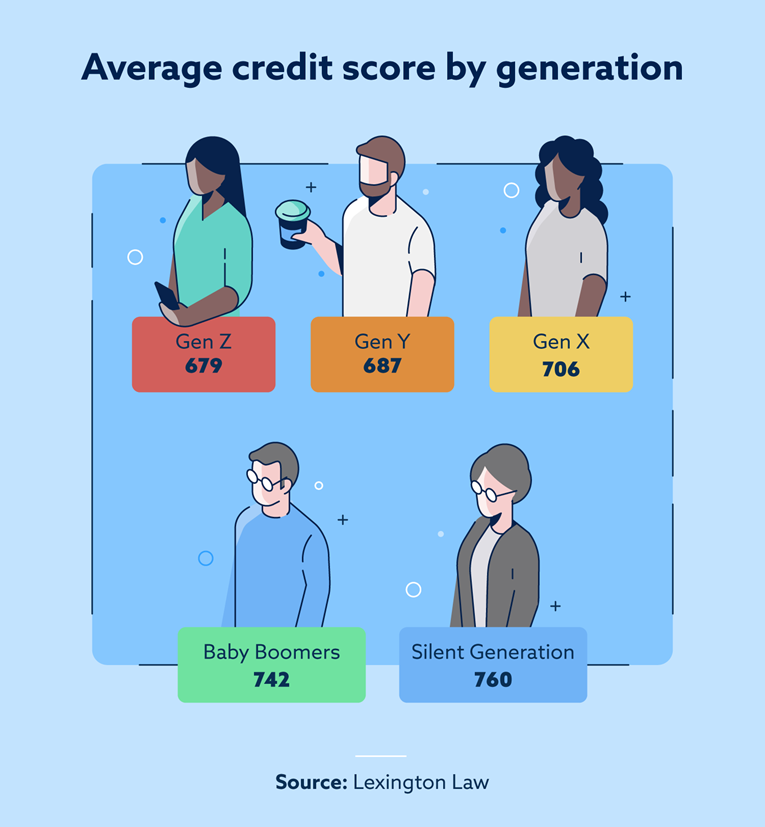
The Average Credit Score in The U.S. in 2023
The current average credit score
As of Q3 2022, the current average FICO credit score in the United States is 714, according to Experian. This average score represents the overall creditworthiness of Americans and serves as a benchmark for comparing individual credit scores.
Factors influencing the current average credit score
Several factors influence the current average credit score in the U.S. These factors include the overall economic conditions, borrowing patterns, debt levels, and individuals’ credit management practices. A strong economy and financial stability generally lead to higher average credit scores, while economic downturns and financial crises can result in lower average scores.
Highlights of the Q3 2023 credit score report by Experian
The Q3 2023 credit score report by Experian provides valuable insights into the credit trends and behaviors of Americans. It highlights any changes in the average credit score, delinquency rates, credit utilization, and other key factors affecting credit health. This report can help individuals understand the current state of credit scores in the U.S. and make informed decisions regarding their own credit management.
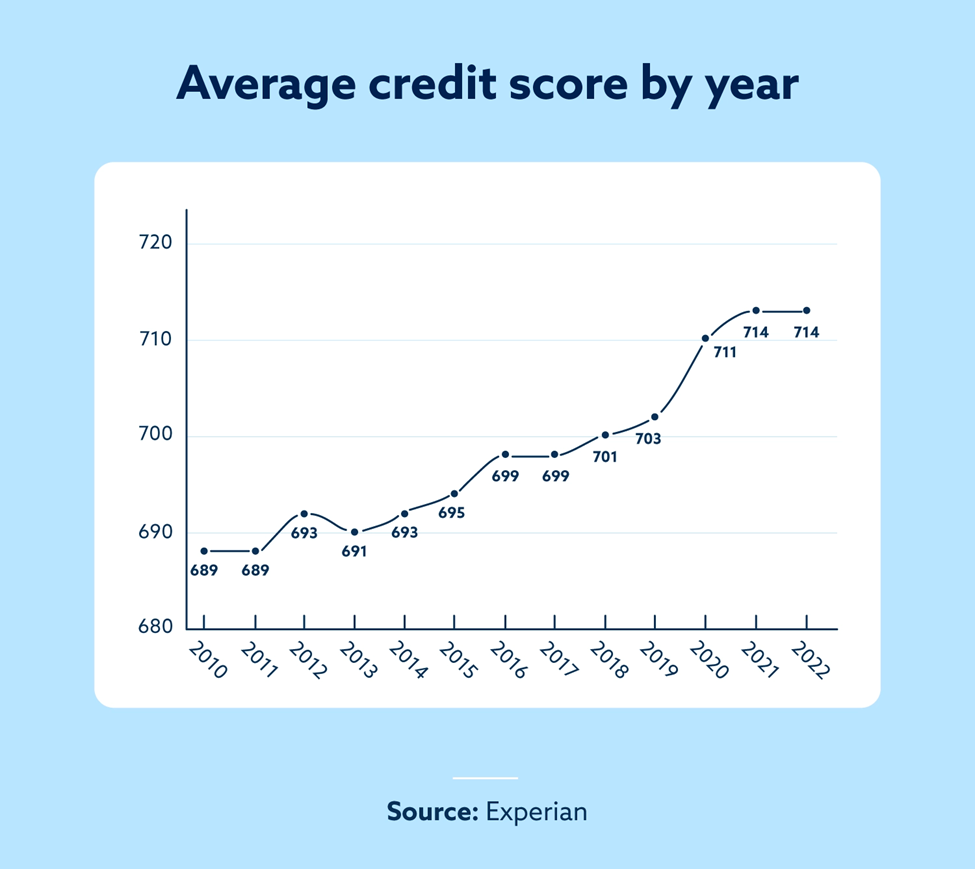
The Progression of Average Credit Score Over the Years
Historical trends in average credit score
The average credit score in the U.S. has seen fluctuations over the years. Prior to the 2008 recession, average credit scores were relatively stable and showed a gradual increase. However, the recession caused a significant decline in credit scores as many individuals faced financial hardships and defaulting loans. Since then, the average credit score has been on the rise as the economy recovered.
Impact of the 2008 recession on average credit score
The 2008 recession had a profound impact on the average credit score in the United States. As the recession led to widespread job losses, foreclosures, and bankruptcies, many individuals struggled to meet their financial obligations. This resulted in a sharp drop in average credit scores as lenders tightened their lending criteria and individuals faced difficulties in maintaining good credit.
Gradual rise in average credit score post-recession
Since the recession, the average credit score has shown a gradual upward trend. As the economy improved and individuals recovered from the financial crisis, creditworthiness began to improve. People became more cautious about managing their debts and making timely payments, leading to an overall increase in average credit scores.

This image is property of www.lexingtonlaw.com.
Comparing Your Credit Score with The National Average
Understanding where your credit score stands
When assessing your credit score, it’s essential to know where you stand compared to the national average. If your score is above the average, it indicates that you have good creditworthiness. On the other hand, if your score is below the average, it may suggest areas for improvement in managing your credit.
Why comparing your score with the national average is important
Comparing your credit score with the national average can provide you with a broader context for understanding your creditworthiness. It can help you gauge how lenders might perceive your credit risk and whether you might face challenges in obtaining credit or qualifying for favorable terms.
Factors to consider while comparing
It’s important to consider various factors when comparing your credit score with the national average. These factors include your overall financial health, borrowing history, credit utilization, debt levels, and any negative items or derogatory marks on your credit report. By considering these factors, you can gain a better understanding of how your credit score aligns with the national average and what steps you might need to take to improve it if necessary.
The Impact of Monthly Credit Report Updates on Average Scores
How often are credit reports updated
Credit reports are typically updated on a monthly basis by the three major credit bureaus: Experian, Equifax, and TransUnion. Lenders and creditors provide updated information to the credit bureaus, such as payment history, credit utilization, and account balances. These updates are crucial in maintaining accurate credit reports and calculating credit scores.
Impact of monthly updates on individual scores and averages
Monthly credit report updates can have a direct impact on both individual credit scores and the average scores. Any changes in individuals’ credit behaviors, such as missed payments, new credit applications, or changes in credit utilization, can influence their credit scores. These changes, when aggregated across the population, contribute to fluctuations in average scores.
Fluctuation of averages due to monthly updates
Because credit reports are updated monthly, average credit scores can fluctuate from month to month. Changes in individual credit behaviors, economic conditions, and borrowing patterns can all contribute to these fluctuations. It’s important to recognize that these fluctuations are normal and that long-term trends provide a more accurate representation of average credit scores over time.
This image is property of www.lexingtonlaw.com.
How Lenders Use Credit Scores
Role of credit scores in loan approval process
Lenders rely heavily on credit scores when evaluating loan applications. Credit scores provide lenders with an objective measure of an individual’s creditworthiness and the likelihood of repaying the borrowed funds. Higher credit scores indicate lower credit risk and make individuals more attractive borrowers in the eyes of lenders.
How lenders do not rely on national averages
While national averages can provide a general understanding of credit scores, lenders do not solely rely on them when evaluating loan applications. Instead, lenders consider a range of credit scores when assessing creditworthiness. They also take into account other factors such as income, employment history, debt-to-income ratio, and the specific loan requirements.
The range of credit scores lenders consider ‘good’
Different lenders may have varying criteria for defining what they consider a ‘good’ credit score. However, generally, credit scores above 670 are seen as favorable and increase the likelihood of loan approval. Higher credit scores may lead to better loan terms, including lower interest rates and higher loan amounts. It’s important to note that each lender may have its own lending standards and credit score requirements.
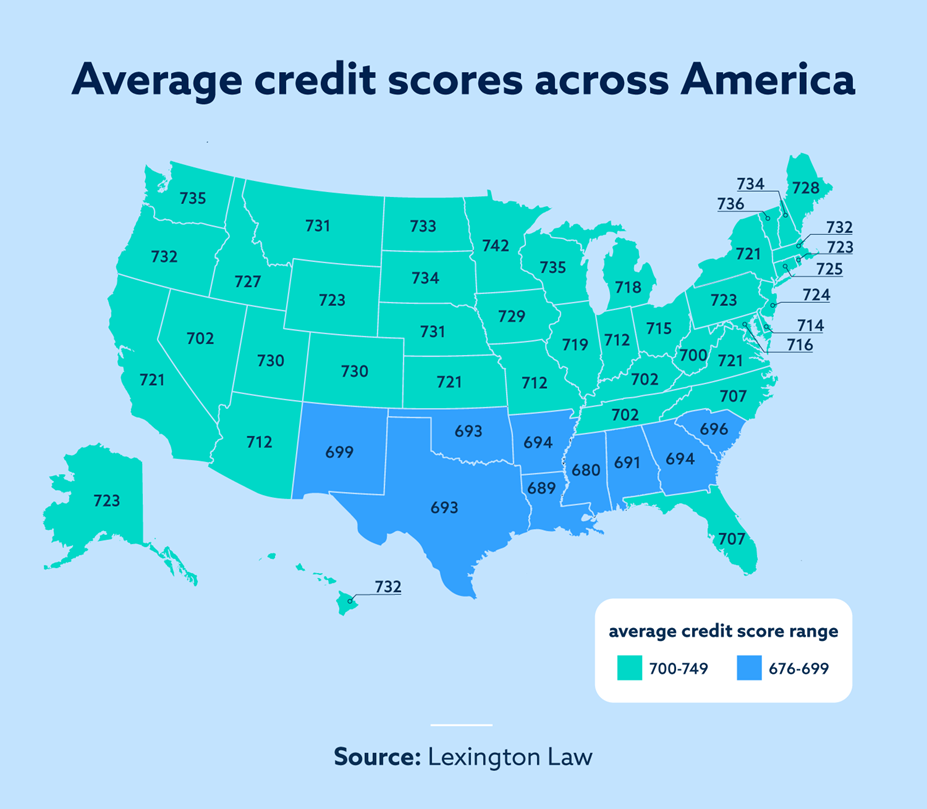
State-Wise Average Credit Scores
States with the highest average credit scores
Credit scores can vary by state due to various factors such as economic conditions, income levels, and financial habits of the residents. Some states consistently have higher average credit scores compared to others. In recent reports, Minnesota has been noted to have the highest average credit score, with an average FICO score of 742. States like North Dakota, South Dakota, and Vermont also tend to have higher average credit scores.
States with the lowest average credit scores
Similarly, some states have consistently lower average credit scores. Mississippi is often reported to have the lowest average credit score, with an average FICO score of 680. Other states with lower average scores include Louisiana, Alabama, and Georgia. These variations in average credit scores among states can be influenced by factors such as income inequality, unemployment rates, and educational attainment.
Factors contributing to state-wise variations in credit scores
State-wise variations in credit scores can be attributed to a combination of factors. Economic conditions, income levels, employment opportunities, and educational resources all play a role in shaping the financial habits and credit behaviors of residents. Additionally, cultural and regional differences in attitudes toward debt, credit utilization, and financial literacy can contribute to variations in average credit scores among states.
This image is property of www.lexingtonlaw.com.
Credit Score Distribution in America
Breakdown of FICO credit score range
Credit scores in America are distributed across various ranges. The FICO credit score ranges, along with the percentage of Americans falling within each range, provide insights into the overall credit health of the population. Here’s a breakdown of the FICO credit score ranges and the corresponding percentages:
- 800-850: 21%
- 740-799: 25%
- 670-739: 21%
- 580-669: 17%
- 300-579: 16%
Percentage of Americans in each credit score range
Based on the breakdown mentioned above, over half of Americans (67 percent) fall within the credit score range of 670 to 850, which is considered good, very good, and excellent. However, 33 percent of Americans have scores below 670, indicating potential credit challenges and less favorable borrowing options.
Understanding the distribution of credit scores in America
Understanding the distribution of credit scores in America helps provide a comprehensive view of the credit landscape. It highlights the percentage of individuals with good credit scores and those who may face difficulties in obtaining credit or qualifying for favorable loan terms. This information can serve as a benchmark for individuals to assess their own creditworthiness and work towards improving their scores if necessary.
Improving Your Credit Score
Effective steps to improve your credit score
If you have a less-than-desirable credit score, there are steps you can take to improve it. Here are some effective strategies:
-
Pay your bills on time: Late payments can significantly impact your credit score. Make it a priority to pay all your bills, including credit card bills, loans, and utilities, on time.
-
Reduce your debt: High levels of debt can negatively impact your credit score. Develop a plan to pay down your debt and avoid accumulating new debt.
-
Keep credit utilization low: Aim to keep your credit utilization ratio below 30 percent. This means using no more than 30 percent of your available credit limits.
-
Diversify your credit mix: It’s beneficial to have a mix of different types of credit, such as credit cards, loans, and mortgages.
-
Regularly check your credit report: Monitor your credit report for any errors or inaccuracies that could be dragging down your score. Dispute any errors you find.
Understanding negative items and their removal
Negative items on your credit report, such as late payments, collections, or bankruptcies, can significantly impact your credit score. It’s important to understand these negative items and their impact on your creditworthiness. In some cases, you may be able to have negative items removed from your credit report through a process known as credit repair.
How to dispute errors in your credit report
If you find any errors or inaccuracies on your credit report, you have the right to dispute them. The Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) allows consumers to challenge any information that they believe to be incorrect or unfairly reported. You can dispute errors by contacting the credit bureaus and providing supporting documentation to prove the inaccuracies. Resolving these errors can help improve your credit score and overall credit health.
In conclusion, understanding credit scores and their significance is crucial in today’s financial landscape. Your credit score impacts your ability to secure loans, obtain favorable interest rates, and access financial opportunities. By knowing how your credit score compares to the national average, understanding credit scoring models, and taking steps to improve your credit health, you can navigate the world of credit with confidence and make informed financial decisions.

This image is property of www.lexingtonlaw.com.