If you’re looking to secure a mortgage loan, understanding your debt-to-income ratio (DTI) is crucial. This metric, used by lenders, determines how much money you can borrow for a mortgage. The DTI is calculated by dividing your monthly payments by your gross monthly income and converting the result to a percentage. While a good DTI for a mortgage is typically below 43%, lenders prefer it to be below 36%. It’s important to note that different mortgage types have different DTI requirements. Lowering your DTI can be achieved by paying off debts, increasing your income, or potentially adding a cosigner. Although DTI does not directly affect your credit score, it is a factor considered by lenders during the mortgage application process.
What is Debt-to-Income Ratio?
When you apply for a mortgage, one of the key metrics that lenders consider is your debt-to-income ratio (DTI). This ratio is used to determine how much money you can borrow for a mortgage and is an important factor in the approval process.
Definition of Debt-to-Income Ratio
Debt-to-income ratio is a measure of your monthly debt payments compared to your gross monthly income. It gives lenders an idea of how much of your income is being used to pay off current debts and helps them assess your ability to take on additional debt. The lower your DTI, the more likely you are to be approved for a mortgage.
How it is Used in the Mortgage Process
Lenders use your DTI to assess your financial stability and determine the risk of lending to you. When evaluating your mortgage application, they will typically look at two types of DTI: the front-end ratio and the back-end ratio.
Why Debt-to-Income Ratio is Important
Debt-to-income ratio is an important metric for both lenders and borrowers. For lenders, it helps them assess your ability to make monthly mortgage payments and determine the amount of risk involved in lending to you. For borrowers, understanding your DTI can help you gauge your eligibility for a mortgage and manage your finances effectively.
Understanding Front-end and Back-end Ratios
When it comes to calculating your DTI, there are two important ratios to consider: the front-end ratio and the back-end ratio. These ratios provide different perspectives on your debt and income and can impact your mortgage approval.
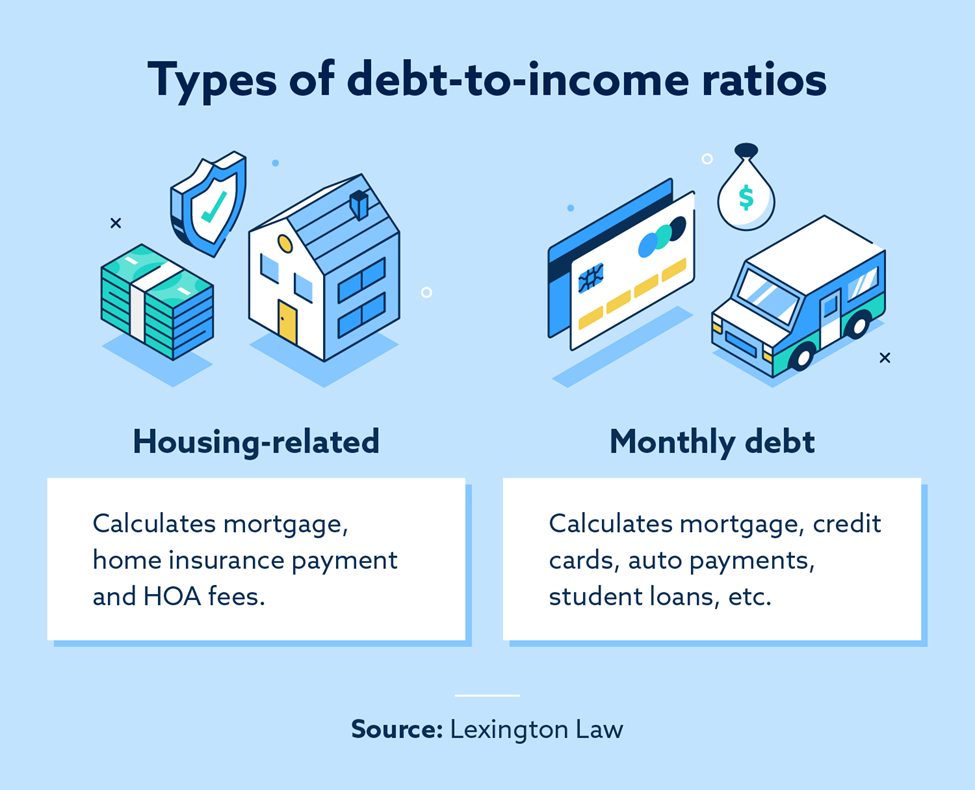
Explanation of Front-end Ratio
The front-end ratio focuses solely on housing-related expenses. It takes into account your monthly mortgage payment, property taxes, homeowner’s insurance, and any homeowner association fees. This ratio is calculated by dividing your total monthly housing expenses by your gross monthly income.
Explanation of Back-end Ratio
The back-end ratio, on the other hand, includes all of your monthly debt payments. In addition to your housing expenses, it also considers other debts such as credit card payments, car loans, student loans, and any other monthly obligations. Like the front-end ratio, the back-end ratio is calculated by dividing your total monthly debt payments by your gross monthly income.
The Difference between Front-end and Back-end Ratios
The key difference between the front-end and back-end ratios lies in the inclusion of non-housing-related debts. While the front-end ratio provides a snapshot of your ability to afford housing, the back-end ratio gives a more comprehensive view by considering all of your monthly debt obligations. Lenders typically consider both ratios when evaluating your mortgage application.
This image is property of www.lexingtonlaw.com.
Calculating Debt-to-Income Ratio
Now that you understand the different ratios involved, let’s explore how to calculate your debt-to-income ratio. While the math involved may seem daunting, it is actually a simple calculation that can be performed with a few basic steps.
The Maths Involved in Calculating DTI
To calculate your DTI, you need to add up all of your monthly debt payments, including your housing expenses and any other debts. Next, you divide this total by your gross monthly income. Finally, you multiply the result by 100 to convert it to a percentage.
Using Gross Monthly Income in the Calculation
Your gross monthly income refers to your total income before any deductions, such as taxes or other withholdings. By using your gross monthly income, lenders can assess your ability to handle debt without accounting for individual deductions or variations in tax rates.
Converting the Result to a Percentage
Once you have divided your monthly debt payments by your gross monthly income, you will have a decimal value. To make it easier to understand and compare, it is common practice to multiply the result by 100 and express it as a percentage. This percentage represents your DTI and is a useful tool for both borrowers and lenders.
Ideal Debt-to-Income Ratio for Mortgage Loans
While there is no one-size-fits-all answer, there are general guidelines that lenders use when evaluating your DTI for a mortgage. Understanding these guidelines can help you gauge your eligibility for a mortgage and set realistic expectations.
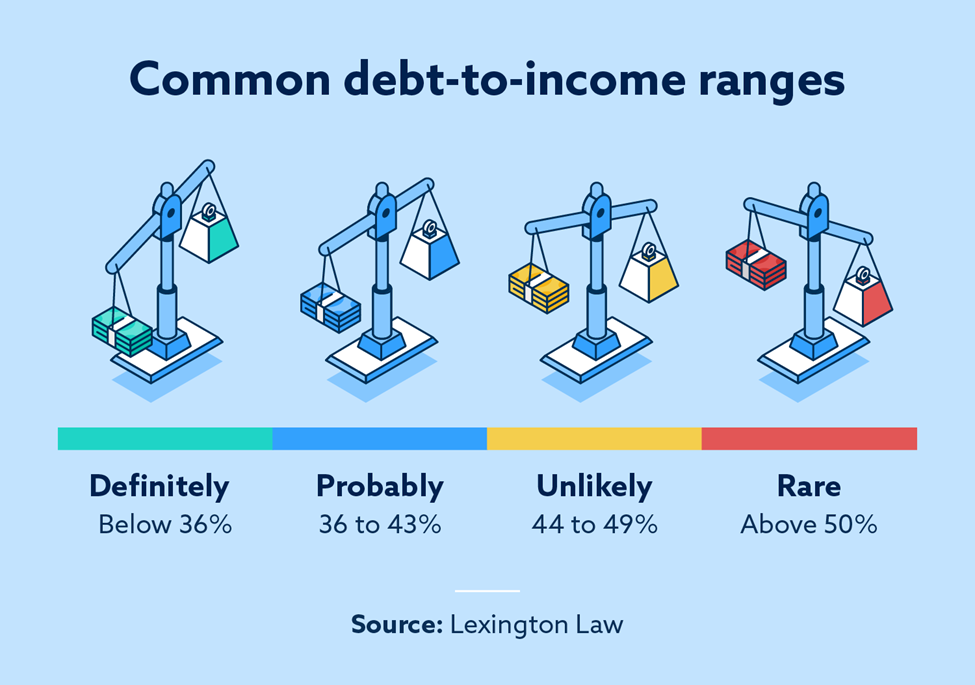
Typical DTI Percentage for Mortgage Approval
A good rule of thumb is to aim for a DTI below 43%. Lenders generally consider a DTI of 43% or lower to be acceptable, as it leaves enough room for you to comfortably handle your monthly mortgage payments. However, keep in mind that this percentage may vary depending on the lender and the type of mortgage you are applying for.
Why Lenders Prefer a DTI Below 36%
While a DTI below 43% is generally acceptable, many lenders prefer a DTI below 36%. This lower threshold indicates that you have a larger portion of your income available for other expenses and savings. Lenders view a lower DTI as a sign of financial stability, increasing your chances of mortgage approval.
Impact of DTI on Loan Amount Approved
Your DTI can also impact the loan amount you are approved for. Lenders typically determine the maximum loan amount based on a percentage of your income. A higher DTI may result in a lower loan amount being approved, as it suggests a higher level of debt compared to your income.

This image is property of www.lexingtonlaw.com.
Different DTI Requirements for Different Mortgage Types
It’s important to note that different mortgage types have different DTI requirements. Here are a few examples of how DTI requirements can vary depending on the type of mortgage you are applying for.
DTI Requirement for FHA Loans
For borrowers seeking an FHA loan, the Federal Housing Administration typically sets a maximum DTI requirement of 43%. This means that your total monthly debt payments, including your mortgage and other debts, should not exceed 43% of your gross monthly income.
DTI Requirement for USDA Loans
USDA loans, which are designed for low to moderate-income borrowers in rural areas, have a maximum DTI requirement of 41%. This requirement applies to both the front-end and back-end ratios and ensures that borrowers have a reasonable amount of income available for other expenses.
DTI Requirement for VA Loans
Veterans Administration (VA) loans, which are available to eligible veterans and their families, typically have more flexible DTI requirements. While there is no specific DTI limit set by the VA, lenders typically look for a DTI of 41% or lower. However, VA loans also consider residual income, which takes into account your remaining income after all expenses are paid.
Ways to Lower Debt-to-Income Ratio
If your DTI is too high and impacting your chances of mortgage approval, there are several strategies you can employ to lower your DTI and improve your financial profile.
Paying Off Debts to Lower DTI
One of the most effective ways to lower your DTI is to focus on paying off your debts. By reducing your overall debt, you can decrease your monthly debt payments and improve your DTI. Consider creating a strategic debt repayment plan and prioritize high-interest loans to maximize your efforts.
Increasing Income to Improve DTI
Another way to lower your DTI is to try increasing your income. Explore opportunities for additional income, such as taking on a side job or freelance work. Increasing your income can help offset your monthly debt payments and improve your DTI.
The Role of a Cosigner in Reducing DTI
If your DTI is still too high even after paying off debts and increasing your income, you may consider adding a cosigner to your mortgage application. A cosigner with a lower DTI and a strong credit profile can help improve your overall financial profile, making you a more attractive borrower in the eyes of lenders.
This image is property of www.lexingtonlaw.com.
The Role of Debt-to-Income Ratio in Credit Scoring
While your debt-to-income ratio does not directly impact your credit score, it is still an important factor considered by lenders during the mortgage application process. Understanding the relationship between your DTI and credit score can help you manage your finances better and improve your chances of mortgage approval.
Understanding Credit Scores
Your credit score is a numerical representation of your creditworthiness. It is calculated based on factors such as your payment history, credit utilization, length of credit history, types of credit, and new credit accounts. A higher credit score indicates a healthier credit profile and increases your chances of obtaining credit or a loan.
How DTI Affects Mortgage Application
While DTI does not directly impact your credit score, it is a factor that lenders consider when evaluating your mortgage application. A high DTI suggests a higher level of debt compared to your income and can raise concerns about your ability to make your monthly mortgage payments. Lenders want to ensure that borrowers have enough disposable income to handle their mortgage obligations.
Why Lenders Consider DTI During Mortgage Application Process
Lenders consider DTI during the mortgage application process because it provides them with insights into your financial stability and ability to take on additional debt. By evaluating your DTI, lenders can assess the level of risk involved in lending to you and determine if you are likely to be able to make your mortgage payments consistently.
How to Improve Debt-to-Income Ratio
If you are concerned about your DTI and its impact on your mortgage application, there are steps you can take to improve your ratio and increase your chances of approval.
Strategies to Lower Monthly Debt Payments
One effective strategy to lower your monthly debt payments is through debt consolidation. Consolidating your debts into a single loan or credit card with a lower interest rate can reduce your monthly payments and improve your DTI. Additionally, you can negotiate with creditors to lower interest rates or develop a repayment plan that better suits your financial situation.
Ways to Increase Gross Monthly Income
Increasing your gross monthly income is another way to improve your DTI. Consider exploring opportunities for a raise or promotion at work, pursuing additional education or certifications to boost your earning potential, or starting a side business or freelance work. Increasing your income can significantly impact your overall financial profile and improve your chances of mortgage approval.
Considering Debt Consolidation
Debt consolidation can be an effective strategy for improving your DTI. By combining multiple debts into a single loan or credit card with a lower interest rate, you can reduce your monthly payments and improve your financial situation. Debt consolidation can make it easier to manage your debts and ultimately improve your DTI.

This image is property of www.lexingtonlaw.com.
Addressing Common Misconceptions about Debt-to-Income Ratio
There are several common misconceptions about debt-to-income ratio that can confuse borrowers. By addressing these misconceptions, you can gain a clearer understanding of how DTI works and its impact on your mortgage approval.
Myths About DTI
One common myth about DTI is that a higher ratio always leads to rejection. While a high DTI can raise concerns and impact your approval chances, it does not automatically result in rejection. Lenders consider multiple factors when evaluating your mortgage application and may still approve your mortgage if you have a strong credit profile and stable income.
Facts About How DTI Affects Mortgage Approval
Contrary to popular belief, DTI is not the sole factor that determines mortgage approval. Lenders evaluate multiple aspects of your financial profile, including credit score, employment history, credit history, and debt management. A higher DTI may require additional supporting documentation or a stronger financial profile, but it does not guarantee rejection.
The Relationship Between DTI and Credit Score
There is often confusion about the relationship between DTI and credit score. While both are important factors in the mortgage application process, they are not directly correlated. Your DTI reflects your current debt obligations compared to your income, while your credit score reflects your creditworthiness based on your payment history and credit utilization. Lenders consider both metrics to assess your overall financial stability.
Expert Tips on Managing Debt-to-Income Ratio
Managing your debt-to-income ratio effectively is crucial for maintaining financial stability and increasing your chances of mortgage approval. Here are some expert tips to help you manage your DTI and improve your financial profile.
Financial Habits to Maintain Low DTI
Developing good financial habits is essential for maintaining a low DTI. This includes budgeting effectively, spending wisely, and avoiding unnecessary debt. By making conscious financial decisions and keeping your debt levels in check, you can maintain a low DTI and improve your financial stability.
Importance of Regular Debt Review
Regularly reviewing your debts is a key aspect of managing your DTI. By keeping track of your debts, you can identify any areas of concern and take necessary steps to address them. This may include paying off high-interest debts, negotiating lower interest rates, or consolidating your debts to reduce your monthly payments.
Effects of Large Purchases on DTI
It’s important to consider the impact of large purchases on your DTI. When you make a significant purchase, such as a new car or home renovations, it can increase your monthly debt payments and raise your DTI. Before making any major purchases, evaluate how it will impact your DTI and assess if it aligns with your financial goals.
In conclusion, understanding your debt-to-income ratio is crucial when applying for a mortgage. Lenders use this metric to assess your financial stability and evaluate your ability to handle debt. By managing your DTI effectively, paying off debts, and increasing your income, you can improve your chances of mortgage approval and maintain a healthy financial profile. Remember to regularly review your debts, consider the impact of large purchases, and cultivate good financial habits to keep your DTI in check.

This image is property of www.lexingtonlaw.com.